Author: Sudeshna Ghosh
Introduction to Barrier to Market Entry
In the ever-evolving landscape of global markets, businesses aspiring to establish a strong foothold must navigate a myriad of challenges. Chief among these are the barriers to entry—obstacles that can impede or deter new competitors from entering an industry. These barriers, which can vary significantly across different sectors and regions, play a critical role in shaping the competitive environment and influencing strategic decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the various barriers to entry, providing valuable insights and actionable advice for businesses aiming to overcome these challenges and thrive in new markets.
Decoding the Concept of Barriers to Entry

Barriers to entry refer to the various economic, legal, and operational hurdles that new competitors must overcome to enter and compete effectively in an existing market. These barriers can be both natural and artificial, encompassing factors such as high startup costs, regulatory hurdles, predatory pricing, and the established brand identity of incumbent firms. Understanding these barriers is crucial for businesses as they craft strategies to enter and succeed in new markets.
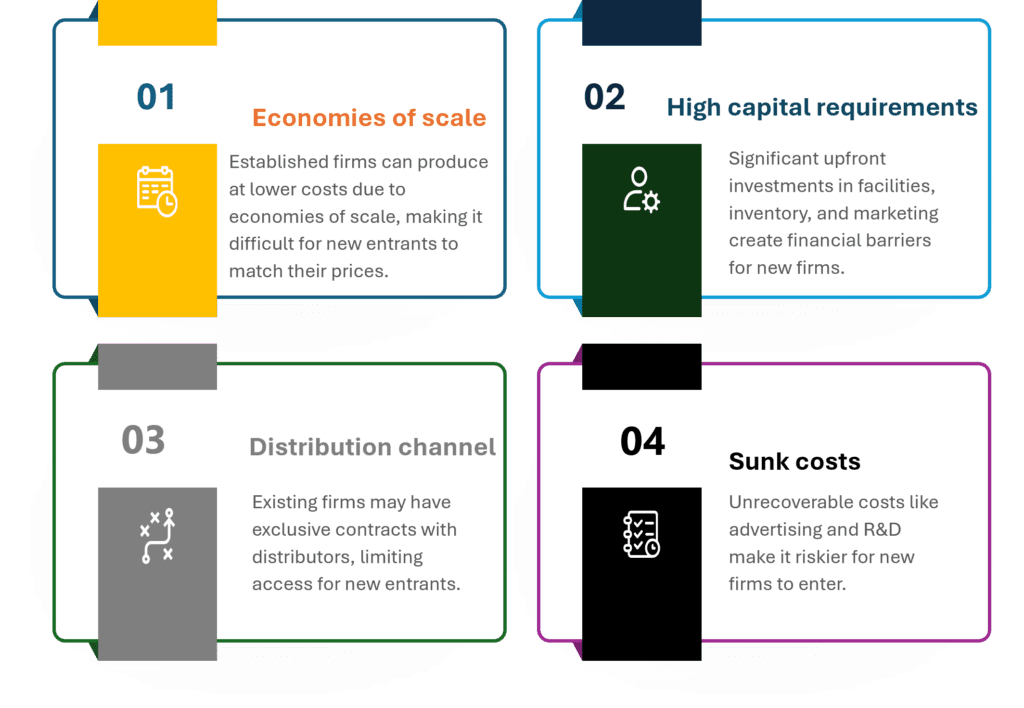
Structural Barriers to Entry in Global Markets
Structural barriers to entry are inherent industry conditions that create significant costs and challenges for new firms looking to enter a market. These barriers can be difficult to overcome and often require substantial resources and strategic planning to navigate successfully.

Strategic Barriers to Entry in Global Markets
Strategic barriers are intentionally created by incumbent firms to deter new competition. These include:

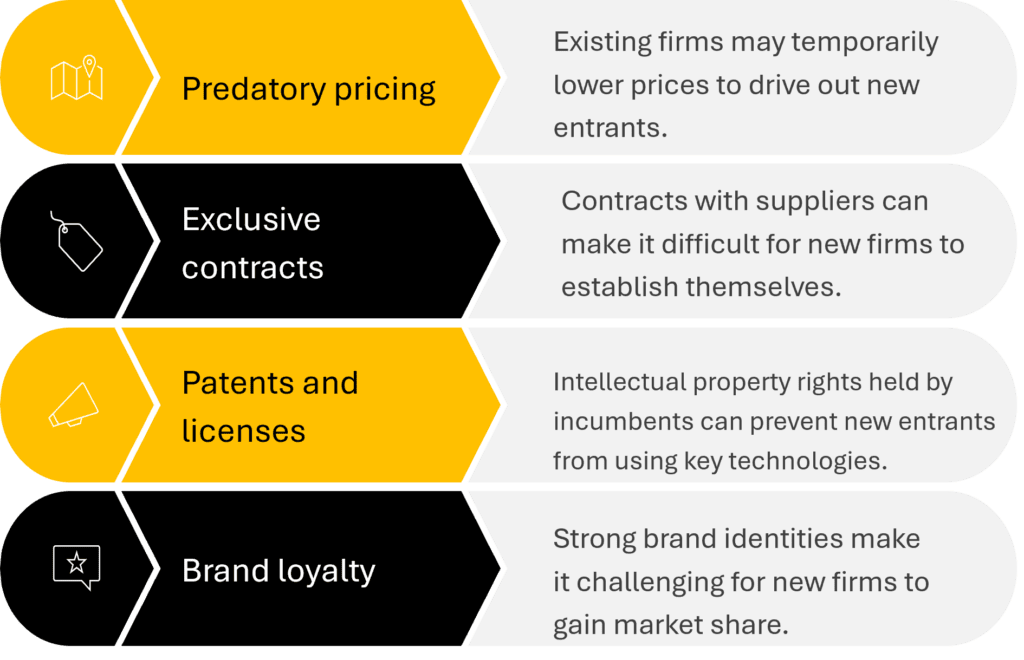
Overcoming these barriers often requires significant investment, innovation, and strategic partnerships. New entrants must carefully analyze the market, identify unmet needs, and develop a compelling value proposition to succeed in the face of these challenges.
Strategies for Overcoming Barriers to Entry
Successfully entering a new market requires strategic planning and a deep understanding of the existing barriers. Here are some effective strategies for overcoming these challenges:


Conclusion
Understanding structural and strategic barriers to entry is essential for successful business market entry and international expansion. Companies must navigate government barriers and adhere to regulatory laws specific to each country and location. Overcoming communication barriers and conducting thorough market research are critical to understanding local market dynamics. These efforts help businesses devise effective strategies to mitigate these barriers and achieve successful entry into new markets.
For businesses looking to navigate the complexities of global market entry, Infiniti Research offers a wealth of resources and expertise. Discover more about our market research solutions designed to help you succeed in competitive markets.
Explore our extensive resources for insights, whitepapers, and case studies on market entry strategies and overcoming barriers to entry.
Ready to take the next step? Contact us today to learn how our customized research and consulting services can support your business goals.


